Table of Contents
In this blog post, we’ll look at how Acne Vulgaris ICD-10 affects diagnosis and therapy, why it matters, and what healthcare practitioners should know about this important classification system. Acne vulgaris, a prevalent skin ailment that affects millions of people worldwide, is sometimes viewed as a minor problem, particularly among teens. However, for healthcare providers, it is far more than just a cosmetic concern. Acne management requires proper diagnosis and treatment, and the adoption of standardized classification systems such as the ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition) helps to ensure consistent and correct medical practice.
What is Acne vulgaris?
Before delving into the technicalities of ICD-10 classification, it is critical to understand acne vulgaris and its clinical implications.
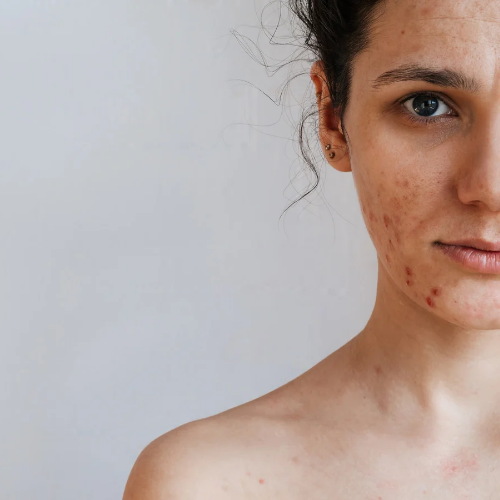
Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts on the face, neck, chest, and back. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, resulting in irritation and the formation of lesions. The syndrome is most common throughout adolescence, but it can last until maturity.

Acne vulgaris can be minor, with a few pimples, or severe, with big, painful cysts. Acne vulgaris can significantly affect a person’s self-esteem, mental health, and overall quality of life, which is why timely and effective treatment is vital.
What is ICD-10?
ICD-10 is an abbreviation for the International Classification of Diseases, tenth edition. It is a standardized method used by healthcare providers around the world to code diagnoses, medical problems, symptoms, and procedures. The World Health Organization (WHO) maintains ICD-10, which is used by hospitals, clinicians, and health insurance providers to assist proper documentation, billing, and reporting of medical disorders.
The ICD-10 system ensures that diagnoses are classified uniformly throughout all healthcare settings. In the case of acne vulgaris, it assists clinicians in determining the severity of the condition, tracking its progression, and managing treatment. For insurers, correct ICD-10 coding is critical for reimbursement.
The ICD-10 code for acne vulgaris
Acne vulgaris has particular ICD-10 codes that healthcare professionals use to diagnose the illness. The codes fall within the broader category of “Diseases of the Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue” (ICD-10 Chapter 12).
The following ICD-10 codes apply to acne vulgaris:
- L70.0: Acne vulgaris.
- L70.1: Acne conglobata.
- L70.2 – acne vulgaris in the teen age group (if mentioned)
- L70.3 – Acne vulgaris in the infantile age group (if specified).
These codes enable healthcare providers to categorize acne according to its severity and patient demographics. The most common and extensively used code for routine instances is L70.0, which denotes typical acne vulgaris.
Impact on Diagnosis
1. Accurate Diagnosis and Documentation
Proper ICD-10 coding allows healthcare providers to accurately document a patient’s condition. Acne vulgaris requires a precise diagnosis for the most effective treatment approach. The L70.0 code allows clinicians to determine the degree and kind of acne, which influences clinical decisions. For example, more severe variants, such as L70.1 (Acne conglobata), may necessitate more rigorous therapies than milder forms of acne vulgaris. Accurate documentation using ICD-10 coding aids in determining whether a patient’s acne is caused by other underlying conditions such as hormonal imbalances or the use of specific medications.
Using ICD-10 codes, healthcare professionals can effectively track acne progression over time, allowing them to adjust treatment protocols as needed. This consistency aids in identifying patterns in patient care, tracking outcomes, and improving long-term management strategies.
2. Differentiating Between Acne Vulgaris and Other Skin Conditions

While acne vulgaris is a relatively simple diagnosis, there are other dermatological disorders that can mimic its symptoms, including rosacea and folliculitis. Acne vulgaris can be differentiated from several other conditions with accurate ICD-10 classification. For example, rosacea can resemble acne at times, but it has a distinct pathophysiology and treatment approach. Using the correct ICD-10 code ensures that the appropriate ailment is diagnosed and addressed, which is critical for both patient outcomes and billing accuracy.
3. Special Populations and Age Groups
ICD-10 codes allow to identify patient demographics. For example, codes like L70.2 for teenage acne vulgaris and L70.3 for infantile acne vulgaris ensure that doctors understand the unique factors at work in different age groups. Adolescents frequently get acne owing to hormonal changes, although neonates may develop acne due to factors such as maternal hormones. These distinctions may influence treatment decisions, as particular medications or approaches may not be suitable for all age groups.
4. Tracking Disease Severity and Type
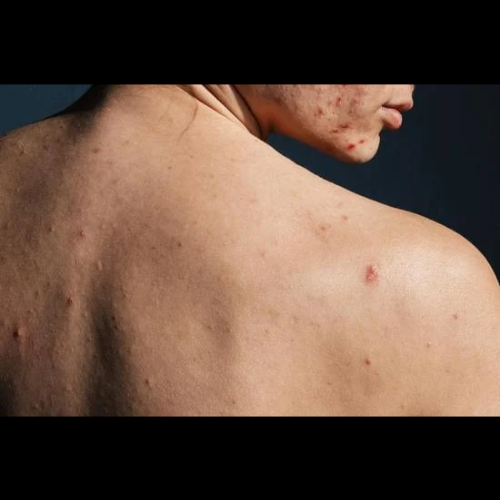
The ICD-10 number also helps track the severity of acne vulgaris. For example, more severe acne, such as cystic acne, may necessitate more specific therapy than mild cases with a few comedones. Providers can utilize the ICD-10 classification to determine whether acne is mild, moderate, or severe, which can help them choose the best treatment option.
5. Ensuring Diagnosis Consistency among Providers
Using a uniform system, such as ICD-10, enhances consistency in diagnosis across multiple healthcare settings. When a patient visits several healthcare practitioners, such as a dermatologist, family doctor, or pediatrician, using the same ICD-10 code ensures that the disease is understood and treated consistently. It also helps to avoid errors or misunderstandings in a patient’s treatment plan, especially when switching between healthcare providers.
Impact on Treatment
1. Managing Treatment Protocols
The ICD-10 code has a direct influence on treatment decisions. Healthcare workers rely on precise diagnostic codes to direct their clinical practice. For example, people with L70.1 (Acne conglobata), a severe type of acne vulgaris, may require systemic medications such as oral antibiotics or isotretinoin, whereas patients with milder variants may simply require topicals. Without appropriate ICD-10 coding, the wrong treatment may be prescribed.
2. Facilitating Appropriate Medication Prescription
The ICD-10 coding system helps determine the appropriate medication for acne vulgaris treatment. Mild acne can be treated with over-the-counter topical treatments like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or topical retinoids, while severe cases may require prescription medications like antibiotics, oral retinoids, or hormonal therapies.
3. Monitoring the Treatment Response
ICD-10 classification is also useful for tracking therapy effectiveness. As individuals undertake treatment for acne vulgaris, healthcare experts will track the patient’s reaction. If a patient’s condition improves or worsens, the relevant ICD-10 code can be modified to reflect the changes. For example, if the acne worsens, the ICD-10 code may change from L70.0 (moderate acne) to L70.1 (acne conglobata) to indicate the illness development.
4. Ensuring reimbursement for services
From an insurance and billing standpoint, precise ICD-10 coding is critical to assuring proper reimbursement for services given. To be reimbursed by insurance companies, healthcare professionals must enter the correct code for acne vulgaris.
Misdiagnosis or miscoding can lead to claim denials, delayed payments, or the need for further documentation. By using appropriate ICD-10 codes, doctors can ensure that their services are compensated in a timely way.
5. Facilitating Patient Education
The adoption of uniform ICD-10 codes also benefits in patient education. Clinicians can provide more thorough information about their patients’ conditions by addressing the exact code linked with their diagnosis. This helps people understand their diagnosis and the therapy options available to them.
6. Personalized Treatment Plans
Each patient’s experience with acne vulgaris is unique. The ICD-10 coding system aids in personalized treatment approaches depending on age, severity, and underlying reasons. For instance, treatment for an adolescent with acne may differ from that for an adult or child, especially when hormonal factors are involved. By identifying these data in the ICD-10 code, clinicians can personalize treatment strategies more efficiently.
Conclusion
ICD-10 codes for acne vulgaris are crucial to ensuring proper diagnosis, treatment, and management of the condition. They assist healthcare practitioners in providing the right care at the right time, as well as facilitating accurate invoicing and compensation. ICD-10 has had a significant impact on acne vulgaris, influencing treatment methods and maintaining consistency in care across numerous providers.
For healthcare providers, understanding the nuances of acne vulgaris ICD-10 codes is vital for offering effective patient care. Using standardized diagnostic codes, doctors may guarantee that they are giving the best possible treatment for each patient based on their specific needs. ICD-10’s function in acne vulgaris diagnosis and therapy goes beyond coding; it is a critical tool that improves overall care quality.
